WNC Orchard Insect Populations
go.ncsu.edu/readext?923227
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲May 1, 2024
 Codling Moth: Apples range from post petal fall to first cover throughout the region, with egg hatching beginning in lower elevations. Cumulative degree-days (DD) range from about 160 in Henderson County to 285 in Cleveland County. With egg hatch underway in lower elevations (e.g., <1500 ft), an initial insecticide targeting codling moth may be necessary if not using mating disruption or not monitoring populations with pheromone traps to obtain information on the intensity of populations. Based on the weather forecast, 250 degree days (beginning of egg hatch) will occur early next week in Henderson County and at similar elevations. With low codling moth populations, which is the case in many orchards, an initial insecticide application can be delayed until about 350 DD (predicted to occur on May 9 in Henderson County).
Codling Moth: Apples range from post petal fall to first cover throughout the region, with egg hatching beginning in lower elevations. Cumulative degree-days (DD) range from about 160 in Henderson County to 285 in Cleveland County. With egg hatch underway in lower elevations (e.g., <1500 ft), an initial insecticide targeting codling moth may be necessary if not using mating disruption or not monitoring populations with pheromone traps to obtain information on the intensity of populations. Based on the weather forecast, 250 degree days (beginning of egg hatch) will occur early next week in Henderson County and at similar elevations. With low codling moth populations, which is the case in many orchards, an initial insecticide application can be delayed until about 350 DD (predicted to occur on May 9 in Henderson County).
In orchards using mating disruption for codling moth, a single insecticide application for first generation codling moth is usually sufficient, and ideal timing is to coincide with TABM control, which occurs at the second or third cover spray.
For insecticide resistance management purposes, do not use insecticides from the same MOA group (see table below) against both the first and second codling moth generation. The second generation will occur in July.
San Jose Scale (SJS): For those growers targeting crawlers, an insecticide targeting this insect should be applied within the next week. The most highly rated insecticides for SJS are Esteem, Centaur, and Movento. Due to insecticide resistance concerns, do not rely on the same insecticide in consecutive years; instead rotate products with different modes of action on an annual basis. Assail also has good activity against SJS, which will further benefit scale control if used over the next several weeks. It should be noted that Esteem and Assail both have activity against codling moth, with Esteem being a good ovicide and Assail providing suppression of adults and larvae.
European Red Mite (ERM): For those choosing a preventive management program for ERM, options include Agri-Mek, Apollo, Savey, Envidor and Zeal. Agri-Mek needs to be applied no later than 1st Cover, and ideally at petal fall. The remaining products should be applied at or shortly between 1st and 2nd cover, and/or before mites increase to 1 or 2 mites per leaf. Again, resistance development is a concern when relying on the same mode of action in consecutive years, so it is strongly recommended to rotate products with different mode of actions on an annual basis (see table below).
| Recommended Insecticides/Miticides Options for Upcoming Sprays | |||
| (Relative Efficacy 5 = excellent, 1= poor, ― no activity or no data) | |||
| Product | Codling Moth | San Jose Scale | Preventive ERM |
| MOA group 4A | |||
| Assail | 4 | 4 | ― |
| MOA group 5 | |||
| Delegate | 5 | ― | ― |
| MOA group 6 | |||
| Agr-Mek | ― | ― | 5 |
| MOA group 7C | |||
| Esteem | 3 | 5 | ― |
| MOA group 10 | |||
| Apollo | ― | ― | 5 |
| Savey | ― | ― | 5 |
| Zeal | ― | ― | 5 |
| MOA group 16 | |||
| Centaur | ― | 5 | ― |
| MOA group 23 | |||
| Envidor | ― | ― | 5 |
| Movento | ― | 4 | ― |
| MOA Class 28 | |||
|
Altacor Exirel Verdepryn |
5 5 5 |
― ― ― |
― ― ― |
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 15 | Apr 22 | Apr 29 | |
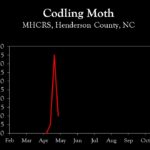
| Codling moth | 0.5 | 4.5 | 1.0 |
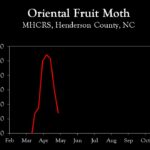
| Oriental fruit moth | 103.0 | 60.0 | 28.5 |
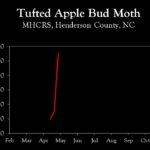
| Tufted apple bud moth | 2.0 | 3.0 | 11.0 |
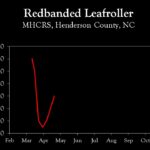
| Redbanded leafroller | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser appleworm | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
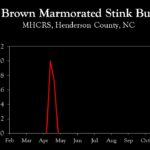
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 |
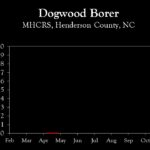
| Dogwood borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
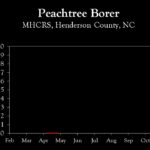
| Peachtree borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
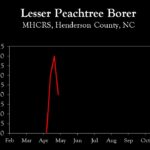
| Lesser peachtree borer | 3.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| San Jose scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Apr 15 | Apr 22 | Apr 29 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: April 15) | biofix | 77 | 139 | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | 288 | 401 | 490 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: April 15) | biofix | 107 | 196 | |
2024 Pest Population Trends
PREVIOUS REPORTS
April 22, 2024
 Petal Fall Sprays and Upcoming Insect Pests:
Petal Fall Sprays and Upcoming Insect Pests:
The cool weather this week has slowed development and activity of key pests targeted at petal fall. This will expand the window for optimum timing of applications until this weekend or early next week.
Target pests at petal fall include plum curculio, oriental fruit moth (OFM) and, if not controlled before bloom, rosy apple aphid. If mating disruption for codling moth and OFM was deployed before OFM started to fly about the third week of March, insecticidal control may not be necessary. The relative efficacy of insecticides recommended at petal fall are shown in the table below. Note that all insecticides recommended at bloom are toxic to bees, so delay petal fall sprays on those cultivars still in heavy bloom, most likely Romes.
Looking ahead over the next couple of weeks, pests to plan for include San Jose scale between petal fall and first cover, preventive control of European red mite and codling moth.
Relative Efficacy of Insecticides for Petal Fall
( ─ no activity, 1 = least effective, 5 = most effective)
Insecticide (activeingredient |
Plum Curculio |
Oriental Fruit Moth |
Rosy Apple Aphid |
Toxicity to Bees |
| Actara (thiamethoxam) | 5 | 2 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
| Assail (acetamiprid) | 3 | 4 | 5 | Moderately Toxic |
| Belay (chlothianidin) | 4 | 3 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
| Avaunt (Indoxacarb) | 4 | 4 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Imidan (phosmet) | 4 | 4 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Verdepryn (cyclaniliprole) | 4 | 5 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Sevin (carbaryl) | 3 | 3 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Voliam Flexi (thiamethoxam + chlorantraniliprole) |
5 | 5 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 8 | Apr 15 | Apr 22 | |
| Codling moth | 0.0 | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| Oriental fruit moth | 108.5 | 103.0 | 60.0 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | 0.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 |
| Redbanded leafroller | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser appleworm | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | setup | 1.0 | 0.7 |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Dogwood borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Peachtree borer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser peachtree borer | 0.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| San Jose scale | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Apr 8 | Apr 15 | Apr 22 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: April 15) | – | biofix | 77 | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | 188 | 288 | 401 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: April 15) | – | biofix | 107 | |
April 15, 2024
Petal Fall Sprays – Have Patience until Bloom Subsides
With a heavy bloom throughout the region, apples vary from full bloom to the petal fall stage. With virtually every orchard containing multiple cultivars, this complicates the timing of petal fall sprays, because both honey bees and wild bees likely will be foraging in the vicinity of drift when spraying. Unfortunately insecticides recommended for key pests at petal fall are highly toxic to bees, so insecticide sprays should be delayed until:
1) >80% petals have dropped
2) bees are not flying in orchards susceptible to drift
3) bees have been removed from orchards
Be sure to check labels on precautions to avoid bee kills, because the wording varies among products.
Relative Efficacy of Insecticides for Petal Fall
( ─ no activity, 1 = least effective, 5 = most effective)
Insecticide (activeingredient |
Plum Curculio |
Oriental Fruit Moth |
Rosy Apple Aphid |
Toxicity to Bees |
| Actara (thiamethoxam) | 5 | 2 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
| Assail (acetamiprid) | 3 | 4 | 5 | Moderately Toxic |
| Belay (chlothianidin) | 4 | 3 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
| Avaunt (Indoxacarb) | 4 | 4 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Imidan (phosmet) | 4 | 4 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Verdepryn (cyclaniliprole) | 4 | 5 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Sevin (carbaryl) | 3 | 3 | ─ | Highly Toxic |
| Voliam Flexi (thiamethoxam + chlorantraniliprole) |
5 | 5 | 5 | Highly Toxic |
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Apr 1 | Apr 8 | Apr 15 | |
| Codling moth | setup | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| Oriental fruit moth | 100.0 | 108.5 | 103.0 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | setup | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| Redbanded leafroller | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Lesser appleworm | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | – | setup | 1.0 |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 0.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Dogwood borer | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Peachtree borer | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lesser peachtree borer | setup | 0.0 | 3.0 |
| San Jose scale | setup | 0.0 | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Apr 1 | Apr 8 | Apr 15 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: April 15) | – | – | biofix | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | 137 | 188 | 288 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: April 15) | – | – | biofix | |
April 8, 2024
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Mar 25 | Apr 1 | Apr 8 | |
| Codling moth | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Oriental fruit moth | 35.0 | 100.0 | 108.5 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Redbanded leafroller | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | – | – | setup |
| Lesser appleworm | – | – | setup |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | – | – | setup |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | – | – | setup |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| Dogwood borer | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Peachtree borer | – | setup | 0.0 |
| Lesser peachtree borer | – | setup | 0.0 |
| San Jose scale | – | setup | 0.0 |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
April 1, 2024
Learn more about southeastern apple insect pests at the Apple Insect Management page.
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Mar 18 | Mar 25 | Apr 1 | |
| Codling moth | – | – | setup |
| Oriental fruit moth | 27.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | – | – | setup |
| Redbanded leafroller | 10.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | – | – | – |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dogwood borer | – | – | setup |
| Peachtree borer | – | – | setup |
| Lesser peachtree borer | – | – | setup |
| San Jose scale | – | – | setup |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Mar 18 | Mar 25 | Apr 1 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | 31 | 68 | 137 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |
March 25, 2024
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
–
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Mar 13 | Mar 18 | Mar 25 | |
| Codling moth | – | – | – |
| Oriental fruit moth | 0.0 | 27.0 | 35.0 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | – | – | – |
| Redbanded leafroller | 12.0 | 10.0 | 2.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | – | – | – |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dogwood borer | – | – | – |
| Peachtree borer | – | – | – |
| Lesser peachtree borer | – | – | – |
| San Jose scale | – | – | – |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Mar 13 | Mar 18 | Mar 25 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | – | 31 | 68 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |
2024 Average Weekly Trap Captures
–
| HENDERSON COUNTY | |||
| Insects per trap | |||
| Mar 8 |
Mar 13 | Mar 18 | |
| Codling moth | – | – | – |
| Oriental fruit moth | – | 0.0 | 27.0 |
| Tufted apple bud moth | – | – | – |
| Redbanded leafroller | – | 12.0 | 10.0 |
| Obliquebanded leafroller | – | – | – |
| Lesser appleworm | – | – | – |
| Apple maggot (abandoned and research orchards) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (commercial) | – | – | – |
| Brown marmorated stink bug (unsprayed) | – | – | – |
| Spotted tentiform leafminer | – | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dogwood borer | – | – | – |
| Peachtree borer | – | – | – |
| Lesser peachtree borer | – | – | – |
| San Jose scale | – | – | – |
*Note that these averages illustrate only the timing of insect emergence and fluctuations in populations, and are not representative of population levels in any given orchard. The only way to have an accurate assessment of an individual orchard’s populations is to set up traps in that orchard.
2024 Accumulated Degree Days
| HENDERSON COUNTY | ||||
| Mar 8 |
Mar 13 | Mar 18 | ||
| Codling moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |
| Oriental fruit moth (Biofix: March 15) | – | – | 31 | |
| Tufted apple bud moth (Biofix: TBD) | – | – | – | |